Are you aware of the potential danger lurking behind an enlarged left atrium? Left Atrial Enlargement (LAE) is a medical condition that affects millions across the globe, and symptoms may include shortness of breath or fatigue. If undetected and left untreated, severe complications such as stroke can occur.
In this article, we'll discuss LAE in more detail and provide insight into how it can be diagnosed and treated to stay safe and healthy.
What is Left Atrial Enlargement (LAE)
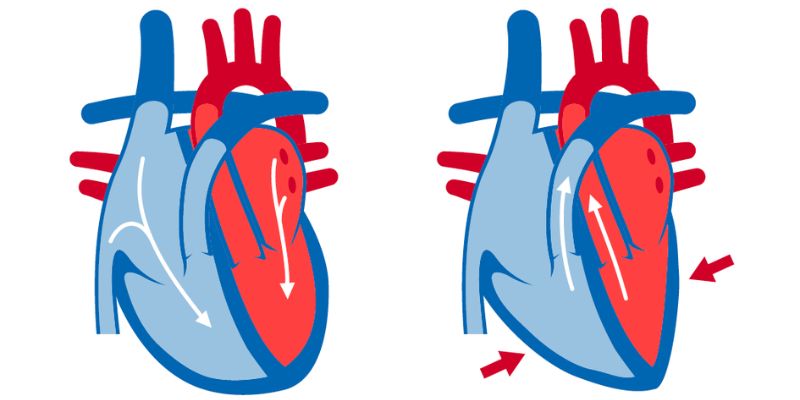
Left Atrial Enlargement (LAE) is an enlargement of the left atrium, a chamber in the heart that receives oxygen-depleted blood from the body. LAE is caused by various factors – high blood pressure, hypertension, and other cardiovascular diseases are some possible causes.
The Symptoms of Left Atrial Enlargement (LAE)
Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath is a common symptom of LAE. This is caused by the enlarged left atrium putting pressure on the lungs, preventing them from expanding properly.
Fatigue
Fatigue is another symptom of LAE, as the heart has to work harder to pump blood through the body due to its increased size. This can lead to exhaustion and an overall lack of energy.
Palpitations or fluttering in the chest
Palpitations, or a fluttering sensation in the chest, are often experienced when suffering from LAE. Irregular heartbeats cause this due to the strain on the heart muscle.
Chest pain
Chest pain is another symptom of LAE, as the increased pressure on the heart muscles often causes pain in this area. This pain can range from mild to severe and should be monitored closely.
Swelling or edema
Swelling and edema (fluid retention) are common among LAE patients. This is often seen in the legs, feet, and ankles due to the strain on the heart muscle.
Heart murmurs
Heart murmurs are extra or unusual sounds heard when listening to your heartbeat. An enlarged left atrium can cause these, as the increased pressure affects blood flow through the heart valves.
Difficulty breathing when lying down
As the enlarged left atrium puts additional pressure on the lungs, those suffering from LAE may experience difficulty breathing when lying down or sleeping. This is because their lungs cannot expand properly in this position.
Feeling faint or lightheaded
Those with LAE often feel faint or lightheaded due to reduced blood flow to the brain. This is caused by the excess strain on the heart muscle, which prevents it from pumping efficiently.
Irregular heartbeat
An irregular heartbeat is another symptom of LAE, as the extra pressure on the heart causes it to beat erratically. This can lead to discomfort in the chest area and should be monitored closely.
Swollen veins in the neck
Swollen veins in the neck are often seen in those suffering from LAE. This is caused by a backup of blood due to an enlarged left atrium, which forces it through the veins in the neck instead of back into the heart.
Diagnosing Left Atrial Enlargement (LAE)
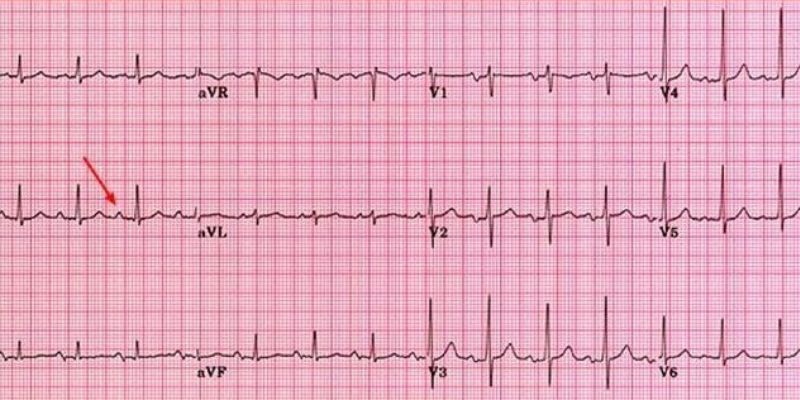
The most common way to diagnose LAE is through an electrocardiogram (ECG). This test records the heart's electrical activity and can detect any changes in its structure, such as an enlarged left atrium. Other tests may include a chest X-ray or echocardiogram. The latter looks at the heart's structure and can provide more detailed information about LAE.
If an LAE diagnosis is confirmed, further tests may be required to determine its cause. These might include blood tests to check hormone levels or an MRI scan to assess heart tissue health. It’s important to accurately identify the cause to provide the right treatment.
The risk of stroke or heart attack associated with LAE can also be assessed using an echocardiogram, Doppler ultrasound, or CT scan. These can indicate how severe the condition is and the level of risk it poses to the patient.
Treating Left Atrial Enlargement (LAE)
Treating Left Atrial Enlargement (LAE) is a difficult prospect, as it requires an accurate diagnosis of its cause and an individualized plan to reduce the risk of stroke or heart attack.
The first step is to manage any underlying conditions that may be causing or contributing to LAE, such as high blood pressure, hypertension, or other cardiovascular diseases. It’s important to take steps such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and eating a balanced diet, all of which can help reduce the risk associated with LAE.
Medications may also be prescribed to control heart rate, reduce fluid retention, improve blood flow, and relax blood vessels. These include diuretics, beta-blockers, and ACE inhibitors.
In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to reduce the size of the left atrium. This is usually done by implanting a device known as an Atrial Septal Defect (ASD) closure device. The ASD closure device creates a one-way valve between the left and right atria, allowing the left atrium to shrink in size and reduce the risk of stroke or heart attack.
In addition to these treatments, lifestyle changes are important for treating LAE. Regular exercise, quitting smoking, and reducing alcohol consumption all help to improve cardiovascular health and reduce the strain on the heart muscle. Additionally, managing stress levels can be beneficial in reducing symptoms associated with LAE.
Benefits of Left Atrial Enlargement (LAE)
Left Atrial Enlargement (LAE) is a serious condition that can cause life-threatening complications if left untreated. However, with the right diagnosis and treatment, reducing the risk associated with LAE and leading a healthy life is possible.
The main benefit of treating LAE is reducing the risk of stroke or heart attack. Making lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and eating a balanced diet can all help to reduce the strain on the heart muscle and improve cardiovascular health.
In addition to this, medications can also be prescribed to control heart rate and relax blood vessels. Surgery may also be necessary in more severe cases, which can reduce the size of the left atrium and reduce the risk of stroke or heart attack.
Taking all the necessary steps to treat LAE makes it possible to lead a healthy and happy life with minimal risk. So if you think you may be suffering from Left Atrial Enlargement (LAE), it’s important to speak to your doctor as soon as possible to get the right diagnosis and treatment. This will ensure your safety in the long run and help you lead a healthier lifestyle.
FAQs
What does LAE mean in ECG?
LAE stands for Left Atrial Enlargement in ECG, an Electrocardiogram abbreviation. An ECG is a test that records the heart's electrical activity and can detect changes such as an enlarged left atrium, which is often seen in those suffering from LAE.
Is left atrial enlargement serious?
Yes, left atrial enlargement (LAE) is a serious condition that can cause life-threatening complications if left untreated. It’s important to seek medical advice if you are experiencing any of the symptoms of LAE, such as shortness of breath or fatigue.
Can you live with left atrial enlargement?
Yes, it is possible to live with LAE. With the right diagnosis and treatment, reducing the risk associated with LAE and leading a healthy and happy life is possible. An important part is making lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and eating a balanced diet. Medications may also be prescribed to control heart rate and relax blood vessels. In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to reduce the size of the left atrium.
Conclusion
Left Atrial Enlargement (LAE) is a serious condition that can lead to life-threatening complications if left untreated. Fortunately, the right diagnosis and treatment plan can reduce the risk associated with LAE and lead a healthy and happy life. This includes making lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, and eating a balanced diet, and medications that may be prescribed to control heart rate and relax blood vessels. In more severe cases, surgery may be necessary to reduce the size of the left atrium.