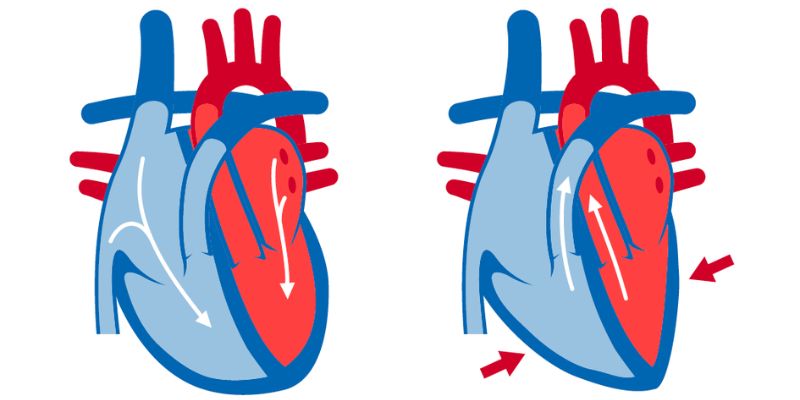
In most cases, we just take one number into account while thinking about our blood pressure. Your blood pressure reading, however, is made up of two numbers: diastolic and systolic.
This is important to recognize because these measurements indicate different aspects of cardiovascular health. By understanding the difference between systolic vs. diastolic blood pressure readings, you’ll gain a deeper insight into your overall heart health and form a better game plan for staying healthy over time.
In this blog post, we’ll explain just what each measurement means in more detail so that you can better understand how to approach maintaining your cardiovascular well-being.
Why Your Blood Pressure Matters
Your blood pressure is an important indicator of your overall cardiovascular health. High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a major risk factor for heart attack and stroke and can increase your risk of developing certain chronic diseases like kidney disease and diabetes. Keeping tabs on your blood pressure numbers can alert you to any issues that may be present and allow you to make the necessary lifestyle changes to keep your heart in good shape.
At its core, the systolic number measures how much pressure your heart exerts when it pumps blood to the rest of your body. The diastolic number measures how much pressure remains in the arteries between heartbeats. A healthy reading for an adult should be 120/80 mmHg or lower.
When readings are higher than this, it could indicate that the walls of your arteries are becoming thickened and hard due to plaque buildup. This causes your heart to work harder to push blood through your body and can lead to several health complications if left unchecked.
Systolic Blood Pressure
Systolic blood pressure is the top or first number of your blood pressure reading and refers to the amount of pressure inside your arteries when your heart beats. It signals how hard your heart is working with each beat, and a healthy level should be 120 mmHg or lower. If this number becomes too high, it can indicate that you have arterial plaque buildup, leading to more serious heart issues if left untreated.
High systolic blood pressure increases the risk of stroke, coronary heart disease, and other cardiovascular problems. Paying attention to this number and making any necessary lifestyle changes to bring it back into a healthy range is important. This may include eating healthier, exercising regularly, reducing stress, and quitting smoking.
High Systolic Blood Pressure
High systolic blood pressure indicates that your arteries have become thickened and hardened due to plaque buildup. This results in your heart working to push blood through the body, causing a ripple effect of health complications if not properly addressed. High systolic blood pressure increases the risk of stroke, coronary heart disease, and other cardiovascular problems.
It is important to pay close attention to this number—as it is the first of the two numbers that make up your blood pressure reading and refers to the amount of pressure inside your arteries when your heart beats. To return it to a healthy level, lifestyle changes are often necessary. These can include eating healthier, exercising regularly, reducing stress, and quitting smoking.
Low Systolic Blood Pressure
Low systolic blood pressure, or hypotension, can be just as concerning as high blood pressure. It is typically associated with dizziness or light-headedness and can strain the heart’s ability to pump enough oxygen around the body. Low systolic blood pressure increases the risk of fainting and falls in seniors, as well as kidney damage and organ failure in extreme cases.
Diastolic Blood Pressure
Diastolic blood pressure is the bottom or second number of your blood pressure reading and refers to the amount of pressure inside your arteries between heartbeats. It signals how much resistance there is in the vessels for your heart to pump against. A healthy level should be 80 mmHg or lower, but if this number becomes too high, it can indicate that you have arterial plaque buildup, leading to more serious heart issues if left untreated.
High diastolic blood pressure increases the risk of stroke, coronary heart disease, and other cardiovascular problems. Paying attention to this number and making any necessary lifestyle changes to bring it back into a healthy range is important. This may include eating healthier, exercising regularly, reducing stress, and quitting smoking.
Low diastolic blood pressure is also known as hypotension and can be just as concerning as high blood pressure. It is typically associated with dizziness or light-headedness and can strain the heart’s ability to pump enough oxygen around the body.
Blood Pressure Ranges
When looking at your blood pressure reading, paying attention to both the systolic and diastolic numbers is important. Knowing your ideal range can help you make more informed decisions regarding lifestyle changes that may improve your cardiovascular health in the long run.
A healthy adult blood pressure range is typically less than 120/80 mmHg. Prehypertensive is a blood pressure range of 120-139/80-89 mmHg, and hypertension is 140/90 mmHg or greater. It’s important to remember that these categories may vary depending on several factors, including age, gender, and race.
For a deeper look into how your blood pressure numbers can affect your heart health, it’s important to consult with your doctor or healthcare provider. They can provide more personalized insight and advice on what lifestyle changes may be necessary to keep your heart in good shape.
Improving Blood Pressure Reading Accuracy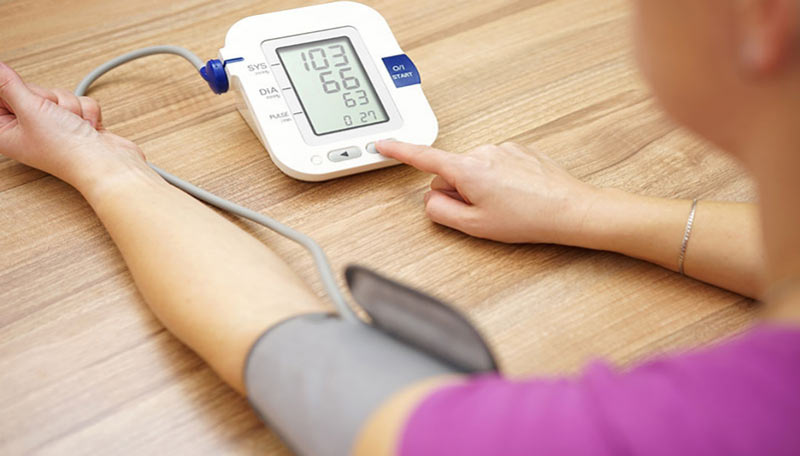
When monitoring your blood pressure, there are a few things you can do to ensure that you get the most accurate readings. First and foremost, it’s important to ensure the cuff size is appropriate for your arm size. It can lead to an inaccurate reading if it is too small or too big. It’s also recommended to take multiple readings in a row and average them for the most accurate results.
Finally, knowing what activities may affect your blood pressure reading is important. This includes eating, drinking caffeinated beverages, smoking, exercising, taking certain medications, and being in certain environments, such as hot or cold temperatures. Being mindful of these variables can help you better understand your heart health.
FAQs
Q: What is the normal range for Blood pressure readings, systolic and diastolic?
A: The normal range for systolic blood pressure is typically less than 120 mmHg, and the normal range for diastolic blood pressure is less than 80 mmHg. However, it’s important to note that these ranges may differ depending on several factors, including age, gender, and race.
Q: What activities can affect my blood pressure reading?
A: Activities that can affect your blood pressure reading include eating, drinking caffeinated beverages, smoking, exercising, taking certain medications, and being in certain environments, such as hot or cold temperatures. Being mindful of these variables can help you better understand your overall heart health.
Q: What are the risks associated with high or low blood pressure?
A: High Blood pressure readings, systolic and diastolic can increase the risk of stroke, coronary heart disease, and other cardiovascular problems. Low systolic blood pressure increases the risk of fainting and falls in seniors, as well as kidney damage and organ failure in extreme cases. Low diastolic blood pressure can lead to dizziness or light-headedness and strain the heart’s ability to pump enough oxygen around the body. Pay attention to your blood pressure readings and consult with your doctor if you have any concerns.
Conclusion
Blood pressure is an important indicator of your overall heart health and can give you key insights into your cardiovascular well-being. By understanding the difference between systolic vs. diastolic numbers, you can form a better game plan for maintaining your blood pressure in a healthy range. Pay attention to your readings and make any necessary lifestyle changes to keep your heart healthy over time.