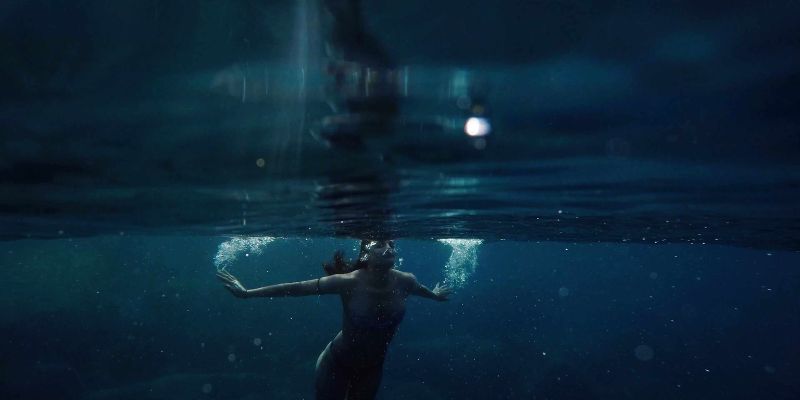
Do you fear the sea? If so, you may have thalassophobia. This anxiety disorder can lead to extreme fear and panic when faced with vast expanses of open water or other bodies of liquid, such as pools or lakes.
Thalassophobia usually stems from a person's subconscious memories and experiences, creating irrational dread that can be difficult to explain.
In this blog post, we'll explore what causes thalassophobia and provide tips on how to cope if you're struggling with it. Keep reading to learn more about this condition.
Symptoms of Thalassophobia
Thalassophobia is more than just an irrational fear of the ocean and can lead to severe anxiety if left unchecked. Common symptoms include difficulty breathing, a racing heart, intense panic or terror when exposed to coastal or deep-water environments, and avoiding activities such as swimming, sailing, or fishing near large bodies of water.
Additionally, individuals who have Thalassophobia may experience stress-related physical symptoms such as headaches, nausea, sweating, and trembling. It is important to note that these are just some common signs associated with Thalassophobia; individual experiences will vary.
If you believe you or someone you know might have Thalassophobia, seeking help from a mental health professional is important. They can create a customized treatment plan to help address the fear and provide the tools necessary to manage it.
Treatment might sometimes include cognitive behavioral therapy, systematic desensitization, hypnotherapy, or medication. With the right support, recovery from Thalassophobia is possible.
The ocean can be a beautiful and calming place, but it can be a source of immense fear and anxiety for those with Thalassophobia. It is important to remember that you are not alone in this struggle, and there is help available. With the right support, recovery from Thalassophobia is possible.
Physical Symptoms of Thalassophobia
While everyone's experience with thalassophobia is unique, some symptoms are commonly felt.
These include:
- Shaking and trembling
- Sweating
- Increased heart rate or heart palpitations
- Dry mouth
- Difficulty breathing, including hyperventilating
- Chest pain2
- Feeling faint, dizzy, or weak
- Nausea or stomach cramps
- Chills
- Numbness or tingling in the hands
Emotional Symptoms of Thalassophobia
Thalassophobia can trigger a panic attack, which may induce symptoms such as:
- Sudden onset of anxiety or fear
- Fear of losing control or dying
Compared to many other specific phobias, thalassophobia may be dangerous. Drowning is a risk when experiencing a panic response while in deep water.
It might help to remember that the panic response is more dangerous than the water. If you know you have untreated thalassophobia, it can also help to always swim with another person or in the sight of a lifeguard.
Diagnosing Thalassophobia

Thalassophobia is a mental health disorder recognized by the Diagnostics and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) as an anxiety disorder.
It is characterized by an excessive fear of large bodies of water, which can manifest in physical symptoms such as sweating, increased heart rate, trembling, shortness of breath, nausea, and even panic attacks.
The symptoms of thalassophobia can be triggered when an individual is exposed to large bodies of water such as the ocean, lakes, and even swimming pools.
A mental health professional will conduct a clinical interview to diagnose thalassophobia and look for certain criteria that meet the DSM-5 guidelines.
This includes observing whether or not the individual experiences intense fear or panic when exposed to large bodies of water and if these feelings are out of proportion to the actual situation.
Other criteria include avoiding activities related to large bodies of water or taking extreme measures to avoid them, as well as experiencing physical symptoms such as sweating, trembling, nausea, and increased heart rate.
If the individual meets all the criteria outlined by the DSM-5, then they may be diagnosed with thalassophobia.
It is important to note that thalassophobia is not simply a fear of swimming or sailing but an intense and irrational fear of large bodies of water that can interfere with the individual’s quality of life.
Treatment options for thalassophobia include cognitive-behavioral therapy, deep breathing exercises, and exposure therapy. With the right support and treatment, individuals can overcome their fear of large bodies of water and live free from this debilitating phobia.
Causes, Triggers, and Risk Factors for Thalassophobia

The causes of specific phobias are not well understood. They may differ from case to case. Some people may develop thalassophobia without a recognized trigger, while others may develop the phobia following a traumatic event.
Nature and Nurture
Many researchers believe that genetic and environmental factors cause specific phobias.3 This means you may be genetically predisposed to a specific phobia, but it may not develop unless you have a traumatic experience or are exposed to triggering events or ideas.
Genetics
Research shows that certain genes are associated with specific phobias, but no studies have examined the genetics behind thalassophobia. However, there is still believed to be a genetic factor to phobias like thalassophobia, following the Darwinian theory of evolution.
Our ancestors were afraid of deep bodies of water, and those who were cautious of the dangers of deep water may likely have lived longer to pass down their genes. This theory is supported by research that indicates that specific phobias are moderately heritable, although the exact percentage can vary.
For example, it has been found that heritability is around 45% for specific animal phobias.
Past Traumatic Events In or Around Water
Traumatic events can also cause thalassophobia. A childhood near-drowning experience, witnessing a shark attack, never learning to swim, or even being told scary stories of the ocean are just a few examples of possible events that could trigger thalassophobia.
By associating a specific situation, such as being in deep water, with a panic response, a phobia of that situation can develop over time.
Upbringing
Some researchers believe that parental behavior may contribute to the development of specific phobias in children. Children with overprotective parents may feel they have limited control over their environment. This can contribute to anxiety and the development of specific phobias.
A parent can also model their fears to their children. For example, a person may develop thalassophobia because a parent openly fears deep water.
FAQs
What causes thalassophobia?
Thalassophobia is caused by a combination of factors, including a fear of the unknown and experiences with traumatic events near or in deep water. It can also be caused by witnessing others experience fear or trauma in the presence of deep water, hearing stories about horror movies involving sea creatures, or developing an irrational fear due to a lack of understanding of the ocean’s environment.
What are the rarest phobias?
The rarest phobias include Agateophobia (fear of insanity), Deipnophobia (fear of dinner conversations), Nomophobia (fear of being without mobile phone coverage), and Thalassophobia (fear of the sea). All these fears are uncommon and can be difficult to diagnose as they often require specialized treatment.
Is thalassophobia a bad thing?
Thalassophobia is not inherently ‘bad’; it’s a normal response to fear and anxiety. However, if left untreated, thalassophobia can become debilitating and interfere with daily life. Therefore, seeking professional help to manage the condition is important.
Conclusion
Though much is still unknown about thalassophobia, it's important to remember the lengthy list of symptoms and possible treatments. Taking steps to prevent and manage this debilitating anxiety disorder is essential for many people who experience it, including contacting a mental health professional, avoiding triggers, changing thought patterns with cognitive-behavioral therapy, reducing stress levels through breathing exercises and physical activity, as well as setting up safe environments for themselves.
Learning more about thalassophobia and how it can be managed is a good idea. Though there are risks and complications associated with thalassophobia, individuals can successfully manage their anxiety by understanding the condition better and seeking help early on.