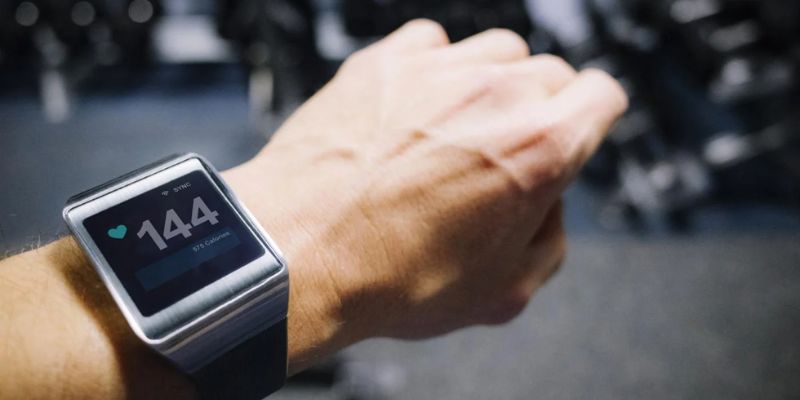
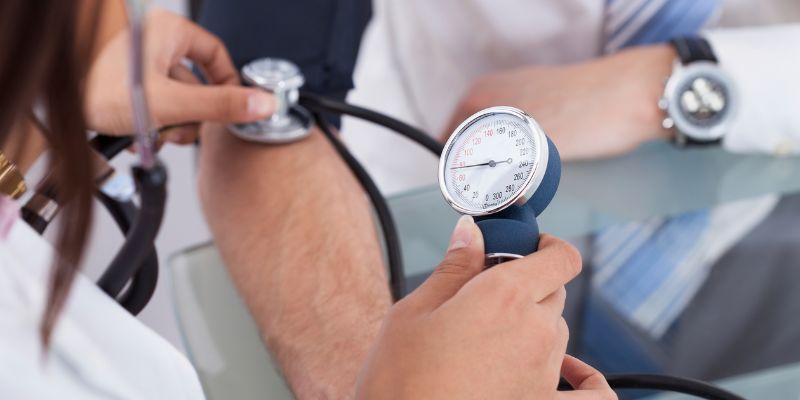
It’s easy to overlook how the heart works and why it is so important. After all, we rarely think about our pumping organs until something goes wrong- but did you know that a dangerous heart rate can indicate underlying health problems?
By understanding what ranges of heart rates are considered unhealthy and taking action if your rate falls into these categories, you can prevent serious medical issues and stay healthy for the long haul. Read on to learn more about a dangerous heart rate and how to prevent it from occurring!
What heart rate is considered "dangerous"?
A dangerous heart rate is typically any heart rate that falls outside the normal range. For adults, this is usually between 60 and 100 beats per minute (BPM). A lower-than-normal heart rate, known as bradycardia, may indicate an underlying medical condition such as hypothyroidism or an infection.
On the other hand, a higher-than-normal heart rate, known as tachycardia, could signal anemia or even a pulmonary embolism. It’s important to note that what constitutes a “dangerous” heart rate varies for each person and can depend on age and activity level.
Ideal and Dangerous Heart Rates
A healthy adult's heart rate is typically between 60 and 100 beats per minute. This range can vary depending on age, gender, activity level, and overall health. For younger adults aged 18-25, a resting heart rate of between 70-90 BPM is generally considered ideal. As people age, their hearts typically beat slower, with an acceptable resting heart rate for those over 65 being closer to 60-80 BPM.
While Exercising
When engaging in physical activity, it’s important to take note of your heart rate. Ideally, the rate should remain within a target range that is specific to each individual. This range is usually between 50-85 percent of your maximum heart rate (MHR). To determine an accurate MHR, you can use a formula of 220 minus your age.
If your heart rate exceeds 85 percent of this figure, you should slow down during exercise and allow it to return to a safe level. If it rises, stop exercising and seek medical advice immediately, which could indicate underlying issues such as arrhythmia.
At Rest
When at rest, a healthy adult's heart rate should remain between 60-100 beats per minute (BPM). A lower-than-normal heart rate could indicate issues such as hypothyroidism and anemia, while a higher-than-normal heart rate could indicate pulmonary embolism. It is important to remember that this range can vary depending on factors such as age and activity level.
While Sleeping
A healthy heart rate should remain between 50-70 BPM when sleeping. Anything above or below this range can be a sign of potential underlying health issues,. Medical attention should be sought if the heartbeat remains abnormal for an extended period.
Dangerous Heart Rates for Adults
A dangerous heart rate for adults is anything outside of the normal range of 60 to 100 beats per minute (BPM). Anything lower than this could signal hypothyroidism or an infection; anything higher might suggest anemia or a pulmonary embolism. It’s important to note that age and activity level can affect what is considered “normal” for each person.
High Rates Causes
High heart rates, or tachycardia, can be caused by various factors. Sometimes, it is simply due to physical activity and stress levels. However, in certain cases, uncontrolled high heart rates can be caused by underlying health conditions such as anemia, thyroid disorders, or various arrhythmias.
Anemia
Anemia is when the body does not produce enough healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen. This means the heart must work harder to pump oxygenated blood around the body due to low oxygen levels. The result is often increased heart rate as the organ pumps faster to compensate for this deficiency.
Thyroid disorders
Thyroid disorders are another common cause of high heart rate. The thyroid gland in the neck produces hormones that regulate metabolism, among other things. When this gland isn’t functioning correctly, it can lead to an imbalance of hormones and higher-than-normal heart rates.
Arrhythmias
Certain arrhythmias, or irregular heartbeats, can also cause dangerously high rates. These arrhythmias occur when the electrical signals that normally prompt the heart to beat become out of sync. This disruption in the rhythm leads to faster-than-normal heartbeat patterns and can be potentially dangerous if left untreated.
High heart rates caused by these conditions should be taken seriously and treated immediately. Suppose you are experiencing any symptoms associated with high heart rates, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or lightheadedness. In that case, it is important to seek medical attention immediately. Doing so can help prevent further complications and ensure you have access to proper treatment for a healthy future.
Risks
There are several risks associated with high heart rates. These include:
1. An increased risk of stroke and heart attack
2. Poor blood circulation
3. Heart failure
4. Abnormal cardiac rhythms
5. Heat exhaustion or heat stroke
6. Decreased exercise tolerance
7. Increased risk of arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation and ventricular tachycardia
8. Cardiac arrest or sudden death
Taking Control of Your Heart Rate
It is important to note that lifestyle changes can help reduce the risks associated with a dangerous heart rate and maintain overall health. This includes regular physical activity, eating a healthy diet, reducing stress, avoiding smoking, and drinking alcohol in moderation.
Additionally, it is important to be aware of any changes in your heart rate and take action if necessary. For instance, if your resting heart rate has suddenly increased or decreased drastically, it may be time to speak with a doctor about potential underlying health issues.
Prevention
The best way to prevent a dangerous heart rate is by staying active and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Regular exercise helps keep your heart strong and healthy by improving cardiovascular function, increasing blood flow, and reducing stress levels.
Eating a balanced diet with plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of developing heart disease. Additionally, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can greatly reduce your risk of developing a dangerous heart rate.
FAQs
Q: What warning signs should I look out for that could indicate my heart rate is too high?
A: Common warning signs may include rapid pulse, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, fatigue, chest discomfort, or pain. It is important to note that these symptoms can also indicate other medical issues, so getting checked out by a doctor if you experience any of them is a good idea.
Q: What should I do if my heart rate is too high?
A: If your resting heart rate falls into the “dangerous” range (greater than 100 beats per minute), it's best to seek help from your physician. Your doctor may suggest lifestyle changes such as physical activity and diet modifications, or they may prescribe medication to regulate your heart rate. In any case, it's important to follow their instructions toto ensure your heart remains healthy and functioning properly.
Q: Are there any long-term effects of a dangerous heart rate?
A: Yes, if left untreated, a dangerous heart rate can lead to serious long-term health issues such as stroke, heart failure, and even death. Therefore, taking action immediately is important if your resting heart rate falls into the danger zone (greater than 100 beats per minute).
Conclusion
The heart is an incredibly important organ, and it's vital to understand what constitutes a dangerous heart rate. By taking action if your rate falls into the danger zone (greater than 100 beats per minute), you can prevent serious medical issues and stay healthy for the long haul.