Are you experiencing thin pain but don't know what could be causing it? Thin pain can have several causes and range from mild to severe, depending on the underlying issue. Today, we'll discuss some possible causes of thin pain so you can feel your best.
We'll provide detailed information about each potential cause, including symptoms and treatments that may help alleviate your discomfort.
By understanding the various factors contributing to a decrease in thickness and associated thin pains, you’ll be equipped with increased knowledge to seek medical advice and take proactive steps towards achieving better health overall.
Identifying the Symptoms of Thin Pain

Symptoms of this pain can vary depending on the cause but may include:
- Pain and Discomfort: This is perhaps the most common symptom of thin pain. It can range from mild to severe and can be localized or widespread.
Additionally, it may be accompanied by other symptoms such as a tingling sensation, numbness, burning sensations, or even muscle weakness in some cases.
- Changes in Skin Sensitivity: Thin pain can often cause areas of skin to become more sensitive than usual, resulting in an increased sensitivity to touch or pressure from clothing or bed linens.
- Visible Changes: In some cases, thin pain can result in visible changes on the skin’s surface, such as discoloration, unusual patches of hair loss, or even ulcerations.
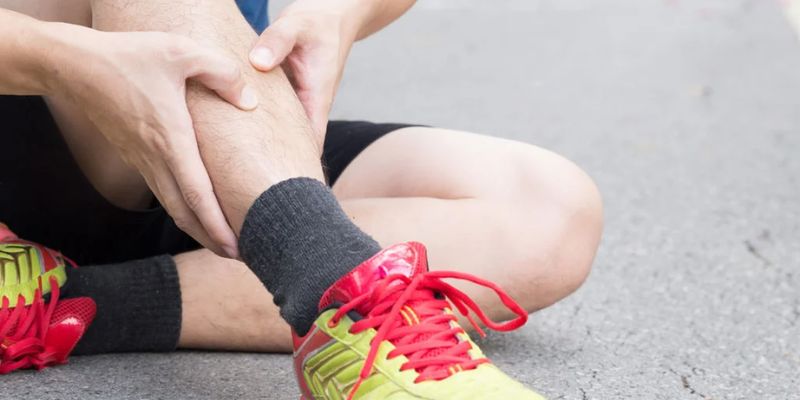
Causes of Thin Pain, such as Inflammation and Injury
1. Inflammation
- Inflammation can cause thin pain due to the body’s natural response to an injury, infection, or irritation. Inflammatory conditions such as arthritis and tendonitis are the most common causes of thin pain.
2. Injury
- Injury is another potential cause of thin pain. Injuries to muscles or ligaments may result in a decrease in thickness that leads to associated thin pains. Trauma from accidents, falls, or overexertion can also lead to thin pains.
3. Diseases
- Certain diseases such as diabetes and lupus can also cause thin pain due to their effect on the skin’s thickness. Additionally, chronic conditions such as cancer can lead to thin pain due to the treatment options and medications used.
4. Neuropathy
- Neuropathy is a condition characterized by nerve damage that can sometimes cause thin pains. Various factors, such as diabetes, alcohol abuse, chemotherapy, infections, or autoimmune diseases, can cause this damage.
5. Medications
- Some medications may also contribute to thin pain if applied directly to the skin or internally. Topical steroids, antibiotics, anti-seizure drugs, and antidepressants are just some medications that may cause thin pains as side effects.
Treatments for Thin Pain
Depending on the cause of your thin pain, various treatments may help reduce your discomfort and improve your quality of life. Common treatment options include:
- Medication: Over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen can relieve inflammation and pain associated with thin pain. Some prescription medications may also be recommended in more severe cases.
- Physical Therapy: Strengthening exercises may be prescribed by a physical therapist to address muscle weakness or other underlying factors contributing to the thin pain.
- Alternative Therapies: Complementary therapies such as acupuncture, massage, and relaxation techniques may benefit some individuals.
- Lifestyle Changes: Making lifestyle adjustments such as avoiding certain activities that cause pain or maintaining a healthy diet can help to alleviate this pain over time.
If your thin pain persists despite trying the above treatments, it is important to consult your doctor to determine the underlying cause and find an effective treatment plan.
With the right approach, you can get back to living life to its fullest without being hindered by thin pain.
Diagnosing Thin Pain
If you've identified that your thin pain is associated with hair loss or thinning on your scalp, book an appointment with your doctor for further evaluation.
Your doctor will likely ask about your medical history and lifestyle habits and perform a physical examination. They may also order blood tests or skin biopsies to confirm the underlying cause of your thin pain.
Managing Thin Pain at Home
1. Self-care
- Taking good care of yourself is essential when managing thin pain. Get enough rest, eat a healthy diet, practice stress-relieving activities such as yoga or meditation, and take breaks from physical activities that cause you discomfort.
2. Applying Heat or Cold
- Applying heat or cold to the affected area can help to reduce inflammation and relieve pain associated with thin pain. You can use hot/cold packs, warm baths or showers, heating pads, ice massages, etc.
3. Using Over-the-counter Medications
- Over-the-counter medications such as ibuprofen and acetaminophen may also manage thin pain. Follow the instructions on the packaging to ensure proper use.
4. Physical Therapy
- Physical therapy and exercises can also be beneficial in alleviating thin pain as they help to increase strength, flexibility, and range of motion in affected areas. Speak with your doctor about what type of physical therapy is best for you based on your needs.
5. Alternative Therapies
- Alternative therapies such as acupuncture, massage, and relaxation techniques may also help reduce thin pain over time. Be sure to speak with a qualified practitioner before trying alternative therapies for managing thin pain.
6. Lifestyle Changes
- Making lifestyle changes such as avoiding certain activities that cause discomfort or maintaining a healthy diet can help to alleviate thin pain.
How Can Diet and Lifestyle Choices Impact Thin Pain?
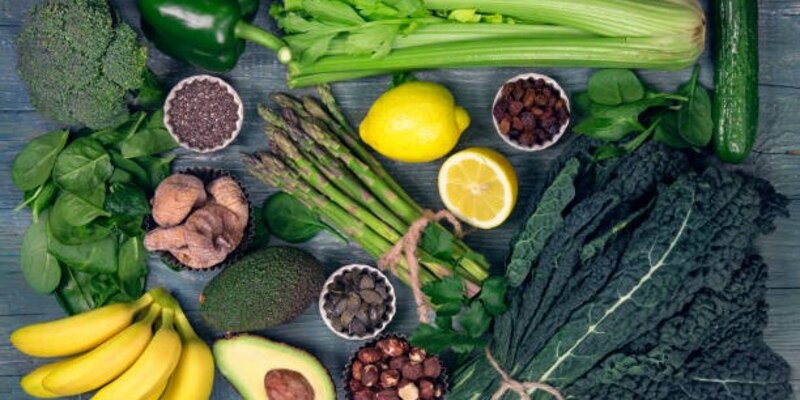
Your diet and lifestyle can play a major role in managing thin pain. Eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and complex carbohydrates can help to reduce inflammation associated with thin pain.
Additionally, avoiding processed foods or those high in saturated fat may be beneficial for reducing thin pain over time.
Other lifestyle factors such as getting enough sleep, avoiding alcohol or nicotine, and engaging in regular physical activity can also help to reduce thin pain.
Additionally, maintaining a positive attitude and practicing stress-relieving activities such as yoga or meditation can provide long-lasting relief from thin pain.
When is it Time to Seek Professional Help for Thin Pain?
If your thin pain persists despite trying the abovementioned treatments, it is important to seek medical assistance. Consulting a doctor or specialist can help you identify the underlying cause and provide an effective treatment plan for managing your thin pain.
With the right approach, you can get back to living life to its fullest without being hindered by thin pain.
FAQs
What are some possible causes of this pain?
Thin pain can have many potential causes, including musculoskeletal injuries, nerve damage, degenerative joint disease, and more. Other causes of thin pain include infections, inflammation, metabolic conditions, or hormonal imbalances.
How can I tell which cause is responsible for my thin pain?
It is best to consult with your doctor when experiencing thin pain. They will be able to assess your symptoms and determine the best course of action for treating the underlying cause. Your doctor may order tests, such as X-rays or ultrasounds, to help diagnose the source of your thin pain.
Are there any treatments available for thin pain?
Treatment options for thin pain will vary depending on the underlying cause. In some cases, lifestyle changes such as stretching, icing the area of pain, and taking anti-inflammatory medications can help manage thin pain.
Other treatments may include physical therapy, massage, or surgery. Speaking with your doctor about the best treatment course for your thin pain is best.
Conclusion
With so many potential causes of thin pain, it's important to talk to your doctor for the best diagnosis and treatment plan. They will be able to identify the root cause of your discomfort and recommend methods for alleviating your thin pain. You can take proactive steps towards feeling better by equipping yourself with knowledge about the various factors contributing to thin pain.




